ADAS Basics and Repair Considerations

After a troubling increase of 7.2% in road deaths in 2015, reported by the NHTSA in August 2016, the importance of technology in making roads safer became even more apparent. This was the biggest jump in road deaths in almost 50 years, with 35,092 people losing their lives. Since human mistakes were a factor in […]
Repair: ADAS and the Automatic Braking System
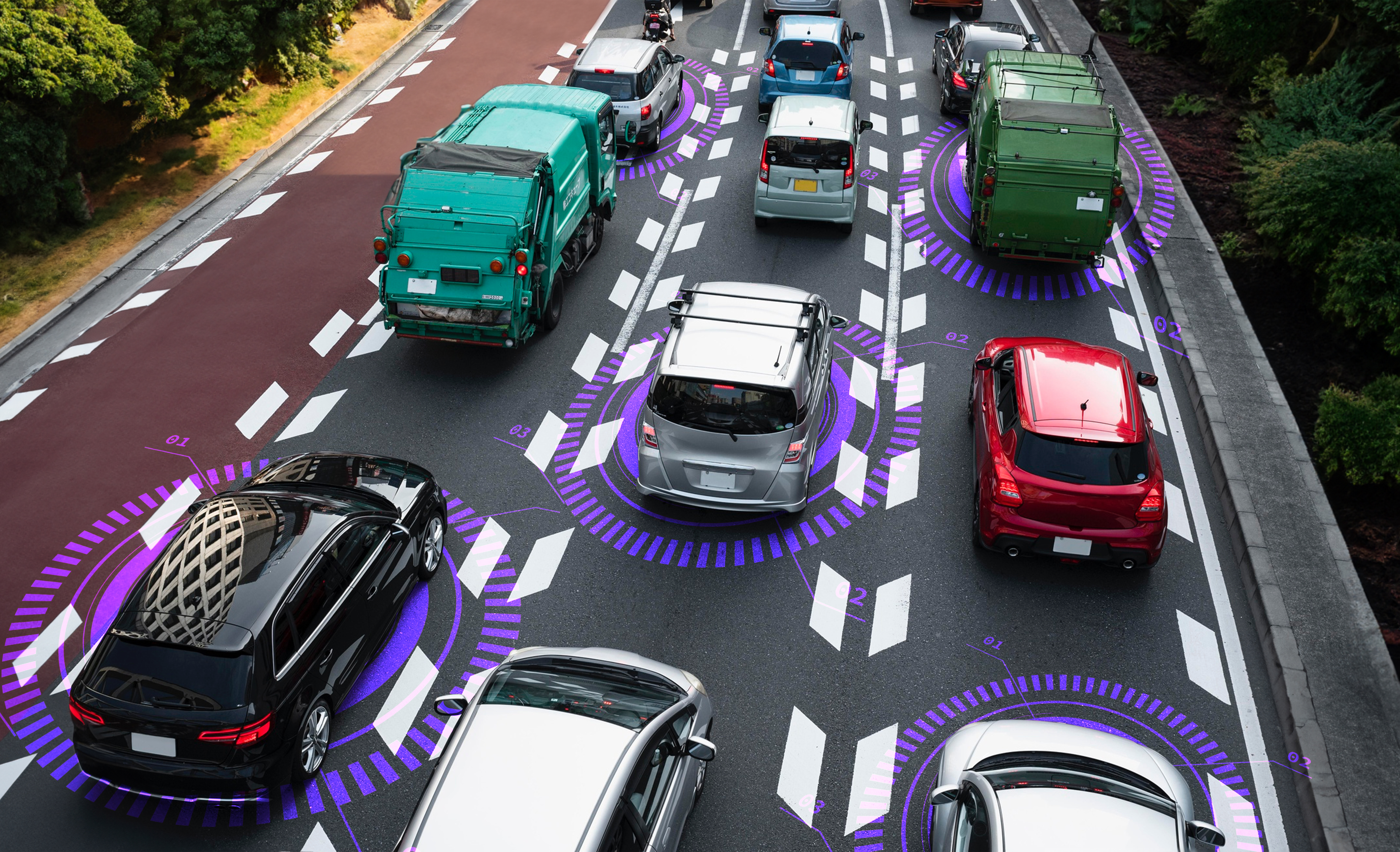
An automatic braking system is a critical component of vehicle safety technology and part of the ADAS ecosystem. It often works with other technologies like pre-collision systems and adaptive cruise control. It is engineered to avert potential collisions or mitigate the impact by slowing down the vehicle when a collision seems imminent. It employs a […]
